
 PDF Index
PDF IndexSDT-base
Contents
Functions

 PDF Index
PDF Index |
Purpose
Material function for piezoelectric solids
Syntax
mat= m_piezo('database name') pl = m_piezo('dbval MatId -elas 12 Name');
See d_piezo Tuto for tutorial calls. Accepted commands are
m_piezo contains a number of defaults obtained with the database and dbval commands which respectively return a structure or an element property row. You can select a particular entry of the database with using a name matching the database entries.
Piezoelectric materials are associated with two material identifiers, the main defines the piezoelectric properties and contains a reference ElasMatId to an elastic material used for the elastic properties of the material (see m_elastic for input formats).
m_piezo('info') % List of materials in data base % database piezo and elastic properties pl=m_piezo('dbval 3 -elas 12 SONOX_P502_iso')
Theoretical details on piezoelectric materials are given in section 1.6. The m_piezo Const and BuildConstit commands support integration constant building for piezo electric volumes integrated in the standard volume elements. Element properties are given by p_solid entries, while materials formats are detailed here.
Supports the specification of a number of patches available on the market. The call uses an option structure with fields
m_piezo('patch') lists currently implemented geometries. In particular
Thus WI28LE14TH_2 is a 28 by 14 by 0.2 mm patch. The geometry can also be coded as 2814TH_2. See 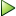 d_piezo('TutoPzMeshingAuto')
for illustration.
d_piezo('TutoPzMeshingAuto')
for illustration.
The piezoelectric constants can be declared using the following sub-types
[ProId Type ElasMatId d31 d32 d33 eps1T eps2T eps3T EDType]
These simplified piezoelectric properties (1.6) can be used for PVDF, but also for PZT if shear mode actuation/sensing is not considered (d24=d15=0). For EDType==0 on assumes d is given. For EDType==1, e is given. Note that the values of єT (permitivity at zero stress) should be given (and not єS).
[ProId Type ElasMatId d_1:18 epsT_1:9]
d_1:18 are the 18 constants of the [d] matrix (see section 6.1.5), and epsT_1:9 are the 9 constants of the [єT] matrix. One reminds that strains are stored in order xx,yy,zz,yz,zx,yx.
[ProId Type ElasMatId e_1:18 epsT_1:9]
e_1:18 are the 18 constants of the [d] matrix, and epsT_1:9 are the 9 constants of the [єT] matrix in the constitutive law (see section 6.1.5).
See also


